anyLogistix scenario stores the data about your supply chain configuration. You can conduct experiments of various types for the created scenario to solve different business tasks.
Each project starts with creating a scenario and populating it with data. Scenario contains complete information on shipping and related operations, as well as all the data on vehicles, warehouses etc. This data is used for running experiments and building reports.
Once you create a scenario in the anyLogistix Professional Server version, you become the creator. Information on the creator is available in the scenario properties to all users with access to the project where this scenario is located.
To create a scenario
-
Click the
 Add button at the right end of the
Scenarios and controls ribbon.
Add button at the right end of the
Scenarios and controls ribbon.
-
Then select
 Create scenario to open the Create Scenario dialog box.
Create scenario to open the Create Scenario dialog box.
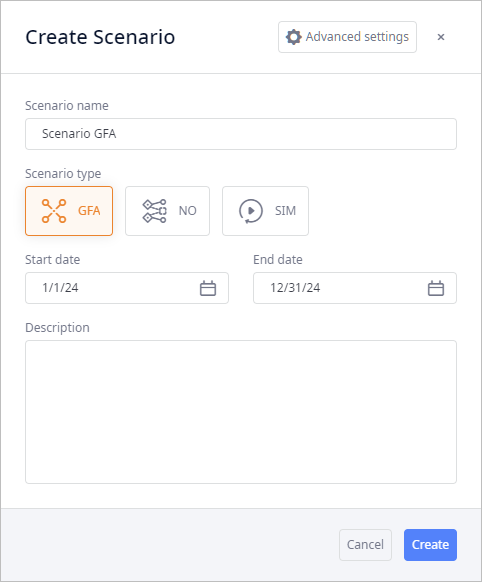
- Define the basic parameters of your scenario. For more information refer here.
-
If required, click Advanced settings to open the advanced section containing scenario settings with editable predefined data.
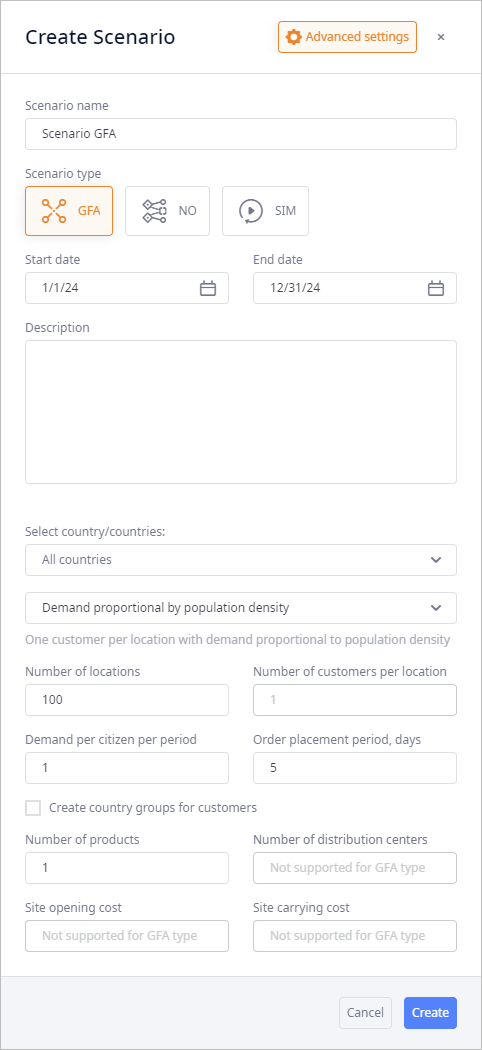
- Provide the required values for the corresponding parameters. For more information refer here.
-
Click Create. The new scenario will be instantly opened.
You can always modify the scenario properties later by right-clicking the scenario and selecting
 Properties from the context menu.
All the currently opened scenarios are available in the scenarios ribbon.
Properties from the context menu.
All the currently opened scenarios are available in the scenarios ribbon.
The error messages may pop up if:
- The Number of distribution centers prevails over the Number of locations.
- The selected countries (or a group of countries) has fewer locations than you specified in the Number of distribution centers parameter (a location in this case is a city with a minimum population of 15000 citizens).
- Advanced settings — opens advanced section containing scenario settings with editable predefined data.
- Scenario name — the name of the scenario that will be displayed in the Scenarios and controls ribbon.
-
Scenario type — defines the type of the scenario that you are creating.
The newly created scenario will be available in the scenarios ribbon.
The list of tables differs for each experiment type.
- Start date – [defines the Start value in the Periods table] scenario starting date and time. It is used for data sampling, and defining simulation experiment starting date.
- End date – [defines in the End value in the Periods table] scenario ending date and time. It is used to define simulation experiment ending date.
- Description – optional field. You can add a comment to the scenario.
- Select country/countries — specify a country or a group of countries that must be involved in this supply chain.
-
Demand proportional to population density — distributes demand within the location(s) of the country/countries according to their population density.
Demand in this case is calculated as population * order size per citizen for the specified period of time, where:
- Population — equals the specified Number of locations, since we have one customer per location. (e.g. 100 locations = 100 customers)
- Order size per citizen — the specified demand of the supply chain per each citizen of the specified number of locations.
- Period of time — the time period during which the quantity of products (specified in the Order size per citizen) is ordered (periodic type of demand).
- Parameters of Demand proportional to population density
-
-
Number of locations — specify the number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
The actual number of locations (cities) in a scenario might be less than expected, since anyLogistix considers cities only with population of 15 000 citizens or more.
- Number of customers per location — specify the number of customers to place at each location within the specified country/countries.
- Demand per citizen per period — the demand of the supply chain per each citizen of the specified number of locations.
- Order placement period, days — specify the number of days in the periodic type of demand.
-
Number of locations — specify the number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
-
Demand distributed by population density — the specified number of customers is distributed within the specified number of locations according to their population density.
Demand in this case is calculated for each location as order size per customer for the specified period of time, where:
- Period of time — the time period during which the quantity of products (specified in the Order size per customer) is ordered (periodic type of demand).
- order size per customer — the demand of the supply chain per each customer (customers are defined in the Total number of customers)
The number of customers for each location is calculated as Max number of locations * k, where:
- Max number of locations — the specified number of locations (cities) the supply chain must have.
-
k — the ratio of the location's population to the total sum of population in the specified
Number of locations up to.
The resulting amount of customers is rounded up to constitute an integer.
- Parameters of Demand distributed by population density
-
-
Number of locations up to — specify the maximum number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
The number of locations that will be created in the scenario may be equal or less than the specified max number. This may happen because population of cities in the specified countries might differ drastically and the resulting number of customers for a particular location might constitute a decimal, which will be rounded up to constitute an integer, thus increasing the number of customers in this particular location and decreasing the overall number of the remaining customers. As a result there might be no customers left for the last (or several) locations. These locations will not be created and the overall number of locations in the scenario will be decreased to the ones with customers.
- Total number of customers — specify the number of customers the supply chain must contain.
- Demand per customer per period — the demand of the supply chain per each customer of the supply chain.
- Order placement period, days — specify the number of days in periodic type of demand.
-
Number of locations up to — specify the maximum number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
-
Equal demand — the specified number of customers is evenly distributed within the specified number of locations.
Demand in this case is calculated for each location as order size per customer for the specified period of time, where:
- Period of time — the time period (periodic type of demand) during which the quantity of products (specified in the order size per customer) is ordered.
- order size per customer — the demand of the supply chain per each customer (customers are defined in the Number of customers per location)
The number of customers for each location is calculated as Number of customers per location * Max number of locations
- Parameters of Equal demand
-
-
Number of locations — specify the number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
The actual number of locations (cities) in a scenario might be less than expected, since anyLogistix considers cities only with population of 15 000 citizens or more.
- Number of customers per location — specify the number of customers to place at each location within the specified country/countries.
- Demand per citizen per period — the demand of the supply chain per each citizen of the specified number of locations.
- Order placement period, days — specify the number of days in the periodic type of demand.
-
Number of locations — specify the number of locations (cities) to create within the specified country/countries (anyLogistix always chooses locations (cities) with the highest population).
-
Create country groups for customers — [Disabled by default] enable to group customers by their location.
New group(s) will be created (in the Groups table) for each country specified in the
Select country/countries option.
The number of groups may be less than the number of specified countries due to significant difference in population size.
-
Number of products — specify the number of products types to create for this supply chain.
If you specify 2 or more products here, then a new Generated products group will be created in the Product Groups table. This group will be used by default in the Demand table.
- Number of distribution centers — [not available for GFA scenario type] specify the number of sites this supply chain must contain.
- Site opening cost — [not available for GFA scenario type] specify the cost of opening a site.
- Site carrying cost — [not available for GFA scenario type] specify the cost of storing products at a site.
-
How can we improve this article?
-

